 In this post we will start to talk about the component that stores the energy from the PV module until it is used: the battery. We will build our system with a lead-acid battery. This post is about the basic function of the battery in our system and the electrical characteristics that are important to us. The next post will be about the different types of lead-acid batteries and how to choose the right type and size.
In this post we will start to talk about the component that stores the energy from the PV module until it is used: the battery. We will build our system with a lead-acid battery. This post is about the basic function of the battery in our system and the electrical characteristics that are important to us. The next post will be about the different types of lead-acid batteries and how to choose the right type and size.
What the battery does in the PV system
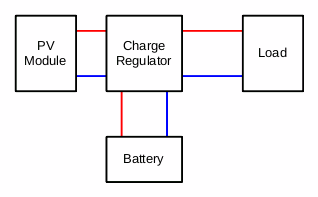 The picture on the left shows again the components of our system and how they are connected. Now let’s look at the battery. Suppose you have good daylight conditions and your PV module sends it’s current into the system. A part of this current flows directly to the load. The rest of the current goes into the battery: The battery is charged by this current that is the difference of the module’s current and the load current.
The picture on the left shows again the components of our system and how they are connected. Now let’s look at the battery. Suppose you have good daylight conditions and your PV module sends it’s current into the system. A part of this current flows directly to the load. The rest of the current goes into the battery: The battery is charged by this current that is the difference of the module’s current and the load current.
On a cloudy day the PV module gives you only littly current. Suppose the load current is higher then the current from the module flows directly to the load. The rest comes from the battery. During the night the load is completely feeded by the battery. In other words: The battery always does ‘the rest’. It stores energy when the current from the module exceeds the load current and it feeds the load partly or completely when the module’s current is too low.
In a typical standalone PV system the battery can feed the load for some days. The capacity should be big enough to handle day and night and also days with good or bad irradiation. This means for the battery that it is charged or discharged with low currents over long periods of time. So the battery should be well-suited for this kind of usage.
Battery characteristics
Now let’s look at those characteristics of the batteries that are important to us:
Capacity
The capacity tells us how much electricity (in ampere-hours) is stored in the battery when it is fully charged. When you multiply the capacity with the system voltage you get the amount of energy stored (in watt-hours).
The capacity varies on the load current, the temperature and the age of the battery. Most important for us is the decrease of capacity during lifetime. This begins very slowly and goes faster the older the battery gets. There are two factors that determine the ‘age’ of your battery: The age in time (years) and the age from usage (cycles, see below). This means that the battery also ages when you keep it fully charged all the time.
Capacity also depends on the load current. With higher current the battery gives you less ampere-hours. This is important only when you have some high-power load for short time repeatedly.
And capacity depends on the temperature. Lower temperature brings you lower capacity. This is important to know when you think about where to put your battery.
Cycle life
One cycle of the battery begins with a fully charged one. Discharge it completely until minimum voltage (e. g. 11V for most 12V batteries) and recharge it. This is a full cycle also called 100% cycle. The cycle life of a battery is the number of full cycles the battery can provide until the capacity has decreased to 80% of the initial capacity. After that point decrease of capacity goes faster and faster.
Lead-acid batteries can provide more cycles when they are not fully discharged. When you have 50% cycles (discharging only half of the capacity and then charging again) you get around two times the number of full cycles. The same with 20% cycles: The battery will lilve for around 5 times as much cycles and so on.
Efficiency
Means the percentage of energy(!) you get when you have put 100% into your battery. This is mostly because the discharge voltage is lower than the voltage during charge time. Different types of batteries vary a lot in efficiency. A low efficiency is a big source of system losses.
Self discharge rate
A fully charged battery gets empty over time by itself. To compensate this you have to charge the battery with some current. This makes you additional losses in your system. Good batteries have a negligable discharge rate regarding our usage.
So now it’s clear how the characteristics of our battery should be: long cycle life, high efficiency and low discharge rate combined with the appropriate capacity. This is what we will talk about in the next post. After that the next steps are the PV module basics, PV module dimensioning, the charge regulator and finally building a system.
Enjoy
heliosoph

Thanks alot this is great information.
Thank you for reading. I am glad when people enjoy what I’m writing.
heliosoph